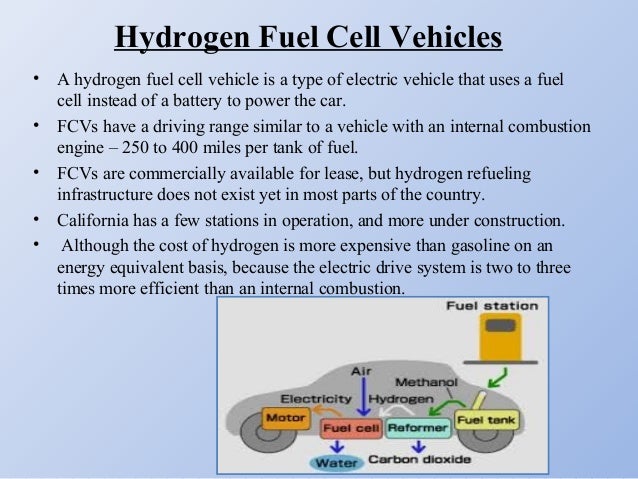
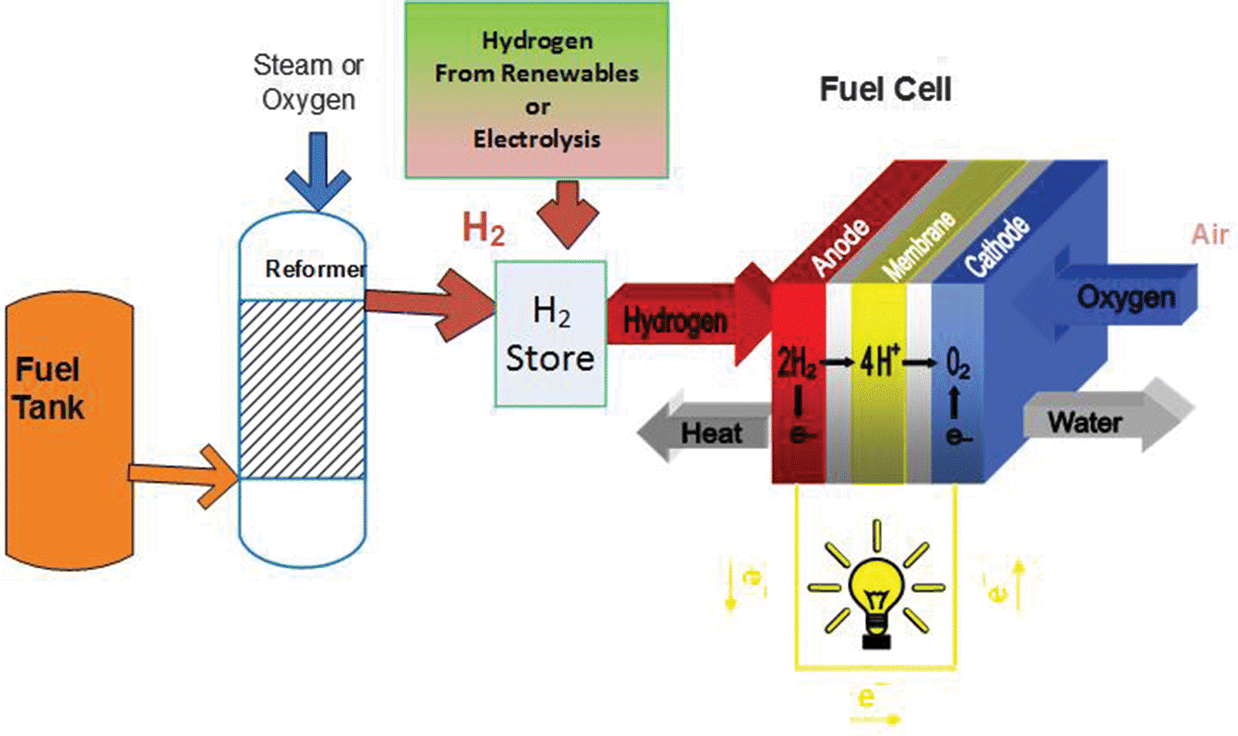
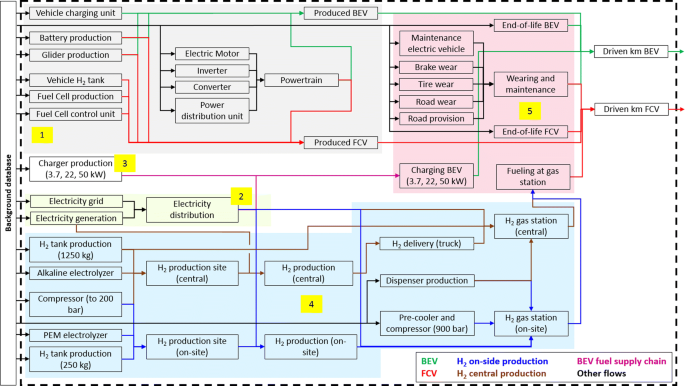
Fuel Cell Tank Definition

Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen usually from air to sustain the chemical reaction whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes.
Fuel cell tank definition. The primary difference between a racing fuel cell and a factory type aluminum fuel tank is the burst strength. Atl bantam fuel cells suba122a 1 586 99. All fuel tanks sold are designed for off road use only in california and are not guaranteed in any way for street use unless specified. It is filled with an open cell foam core to prevent explosion of vapor in the empty portion of the tank and to minimize sloshing of fuel during competition that may unbalance the vehicle or cause.
It is the full responsibility of the end user to determine if. Hydrogen can be stored physically as either a gas or a liquid. Fuel cell gas tank whats the the definition of a fuel cell as known to race car drivers is given above. Racing fuel cell vs.
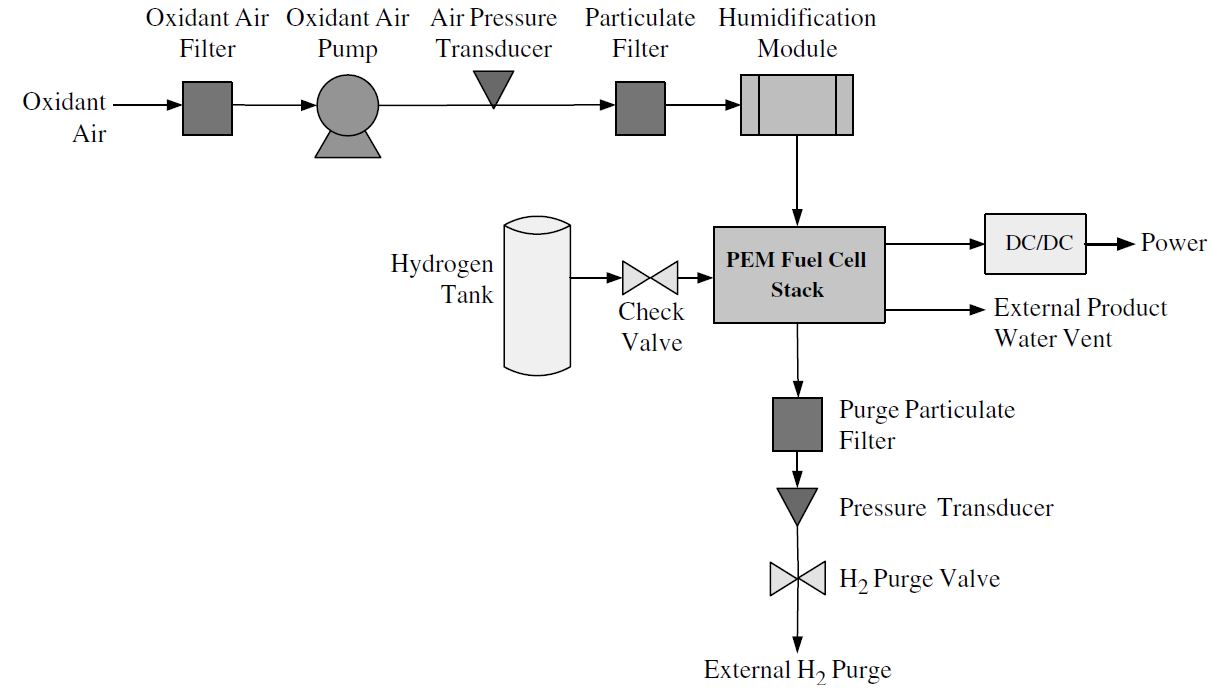
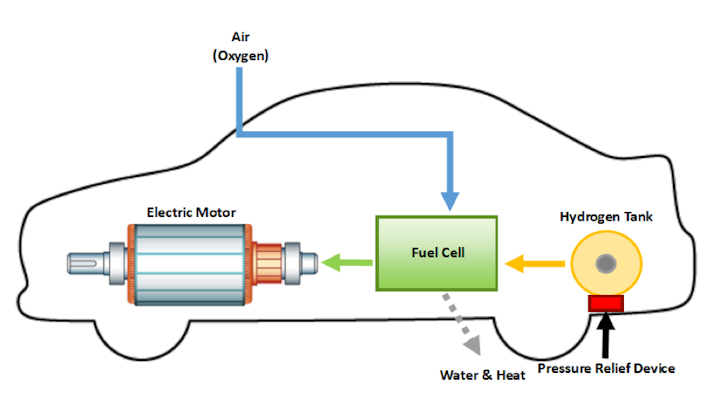
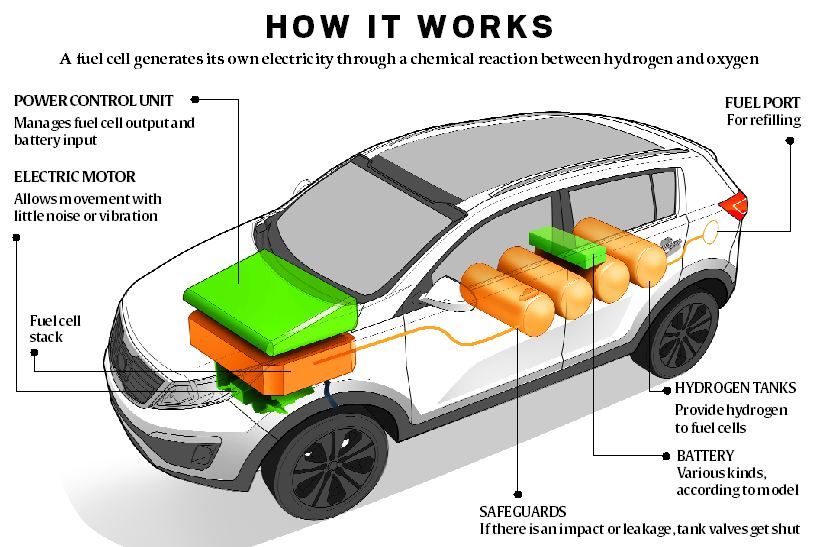
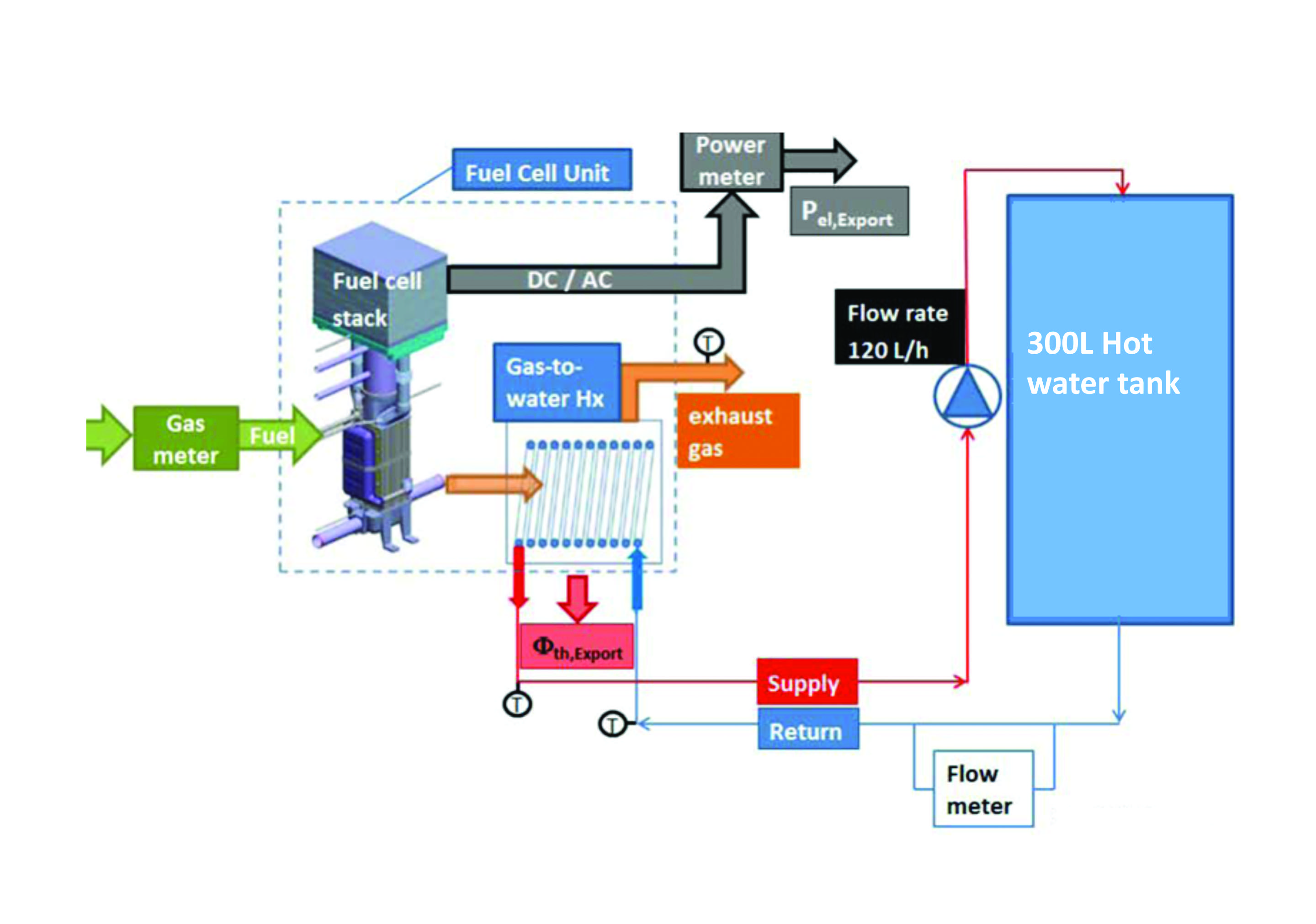
Storage of hydrogen as a gas typically requires high pressure tanks 350 700 bar 5 000 10 000 psi tank pressure. Storage of hydrogen as a liquid requires cryogenic temperatures because the boiling point of hydrogen at one atmosphere pressure is 252 8 c. Ask a scientist or engineer and the answer is. A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel often hydrogen and an oxidizing agent often oxygen into electricity through a pair of redox reactions.
An electrochemical device that continuously changes the chemical energy of a fuel hydrogen and oxidant oxygen directly to electrical energy and heat without combustion. A racing fuel cell has a rigid outer shell and flexible inner lining to minimize the potential for punctures in the event of a collision or other mishap resulting in serious damage to the vehicle. Racing fuel cells are designed primarily for racing and have very high burst strength to prevent race gas from spilling out during a wreck or rollover. The source fuel could be almost anything that can be oxidized including hydrogen methane propane methanol diesel fuel or gasoline.
A fuel cell is a device that produces electricity through a chemical reaction between a source fuel and an oxidant. The only byproducts are water and a small amount of nitrous oxide if air is used.